The 4Cs of diamonds

CARAT WEIGHT
A carat is a unit of measurement used to weigh a diamond. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams. Carat weight is normally referred to in points. One carat consists of 100 points. For example, .50 carats can be labeled as 50 points or 1/2 of a carat. Carat weight is the most important factor when calculating the value of a diamond.
However due to higher or lower quality ratings, diamonds of equal carat weight can often be worth considerably more or less than it’s equal weight counterpart.
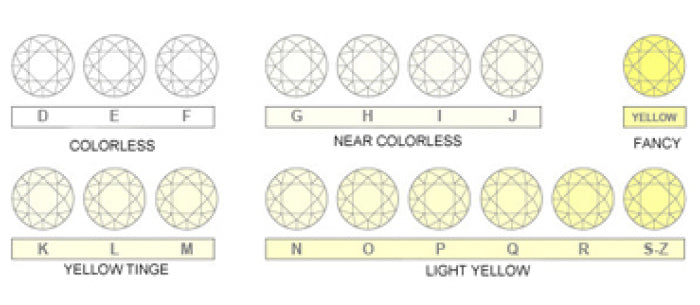
COLOUR
Diamonds come in a wide array of colours which based on it’s rarity, will effect a diamonds value. The most common scale used to rate a diamonds colour is an alphabetical scale starting at the colour D. This is the whitest or purest colour possible in a diamond, also known as pure white. Of course diamonds rated closest to the top of this scale are appraised at a higher value than those with a yellow tint.
Note that fancy colour diamonds are very rare and very expensive, and range in colour from blue to green to bright yellow. They are actually more valuable for their colour.
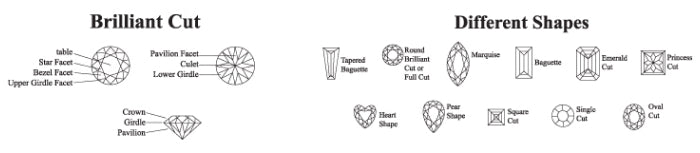
CUT
As is commonly thought, a diamonds cut does not refer to it’s shape. A diamonds cut actually refers to it’s depth and width, and the uniformity of it’s facets. The brilliance of a diamond is heavily dependent on how well the diamond is cut.
A well cut stone will display the fiery colours from deep within the diamond by enabling the maximum amount of light that enters through the table to be reflected back through the table and to the viewer. A poorly cut diamond will absorb light through the diamonds
table and emit the light through the sides, rather than reflecting it back through the top of the diamond. This lower level of reflected light ultimately effects the diamonds sparkle or fire.

CLARITY
Diamond clarity is ascertained by examining internal features, referred to as inclusions, and external characteristics known as blemishes. These attributes arise during the diamond's formation under extreme heat and pressure.
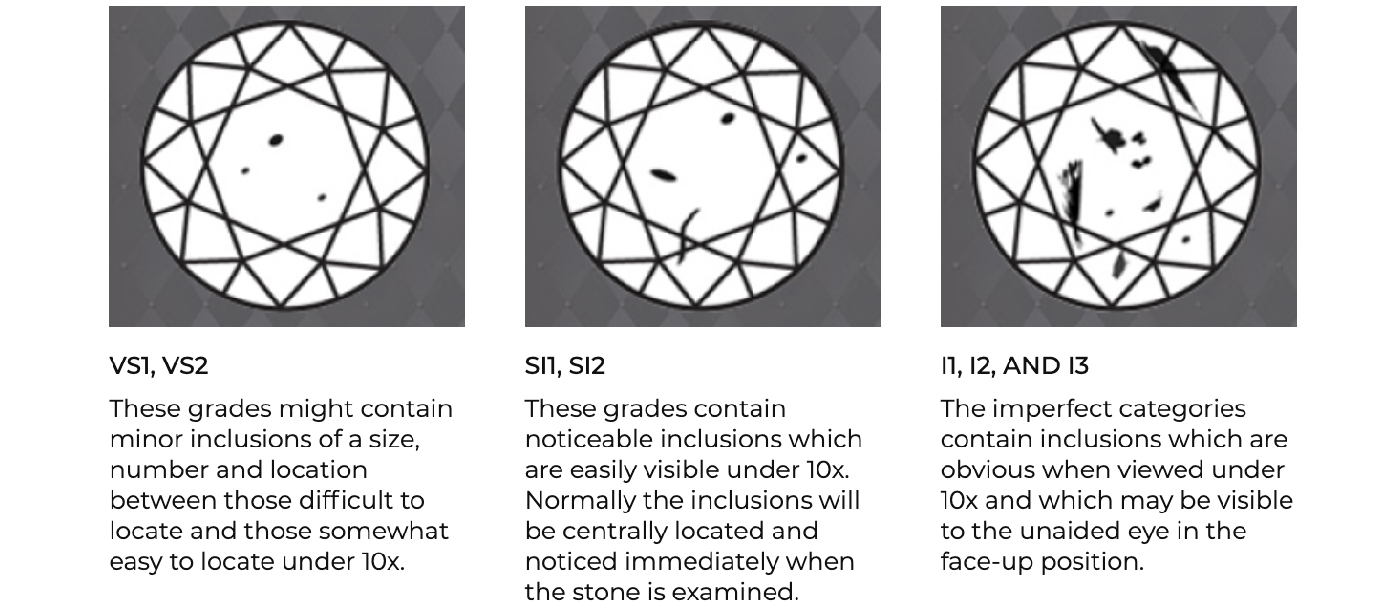
CLARITY
The assessment of a diamond's clarity considers various factors, including the quantity, size, relief, nature, and location of these features, along with their influence on the diamond's overall visual appeal.
While attaining complete purity is unattainable in diamonds, the nearer a diamond approaches flawlessness, the greater its clarity rating.
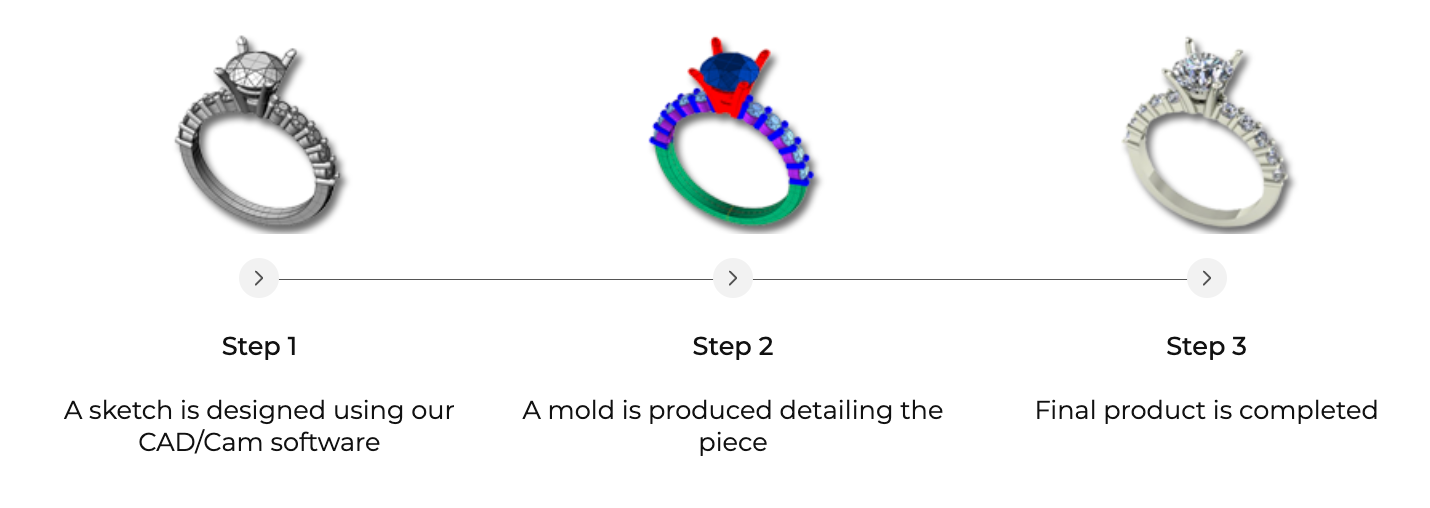
CUSTOM DESIGN
3 STAGES OF MAKING A RING
Over the years, we have developed our jewellery design and manufacturing skills, enabling us to customize your creations using CAD/Cam technology according to your specifications.


